Tesla’s Expansion in Japan Boosted by New EV Subsidies
The recent announcement from the Japanese government regarding revised subsidies for eco-friendly vehicle purchases heralds a significant opportunity for electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers, with Tesla leading the charge. As the landscape for EVs evolves, the impact of these policy changes is expected to reshape the automotive market in Japan, particularly for foreign players like Tesla.
Government Initiatives and Their Implications
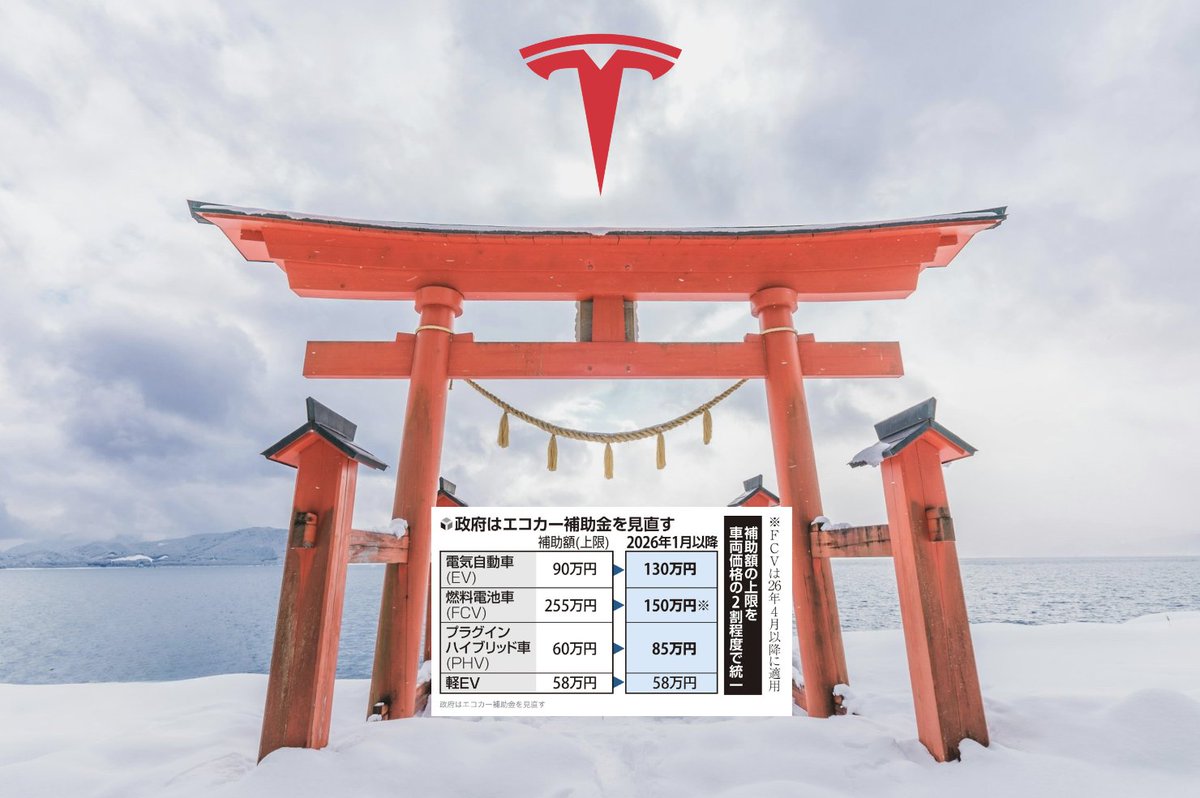
The decision to revise Japan’s subsidy program aligns with broader efforts to become a pioneering hub for sustainable transportation. By raising the subsidy cap for electric vehicles by ¥400,000, the Japanese government is effectively decreasing the cost barrier for consumers, making EVs more accessible than ever. The new subsidy framework, effective January 2026, aims to standardize support across different eco-car categories, aligning with international trade agreements.
The subsidy adjustment, however, is not without its detractors. Fuel Cell Vehicles (FCVs), long seen as a competitive alternative in Asia, will face cuts in subsidies. This revised policy highlights a shift in focus towards promoting battery electric vehicles (BEVs), where brands like Tesla are set to benefit significantly.
Tesla Gains Traction with Strategic Moves
As Tesla experiences accelerating sales momentum in Japan, with a 70% increase in units sold during the first half of 2025, the company is capitalizing on favorable conditions. With its market-leading Model Y, Tesla has emerged as the dominant player in the non-kei car segment. The company’s commitment to expanding physical store locations from a largely online retail model reflects a strategic pivot aimed at enhancing consumer engagement. This retail expansion, coupled with a strengthened Supercharger network, addresses critical infrastructure challenges frequently cited by Japanese consumers.
Domestic Brands Face A Challenging Landscape
While Tesla ramps up its operations, local brands such as Nissan and Toyota face hurdles. Nissan’s Leaf experienced a substantial decline, with sales dropping by 32% in Q1 2025. Though Toyota’s bZ4X saw improvements in later months, it has consistently lagged behind in capturing market share. This juxtaposition of performance among domestic and foreign brands sparks important discussions on competitive strategies and innovation in the Japanese automotive industry.
Policy Revelations Reshape Competitive Dynamics
The newfound balance in subsidy support resonates with criticism from the U.S. Trade Representative (USTR) over previous non-tariff barriers. By leveling the playing field, Japan is fostering a competitive environment that allows BEVs to flourish alongside FCVs. This shift is perceived as a win not only for Tesla but for a broader coalition of foreign manufacturers seeking to penetrate the Japanese market.
Long-Term Implications for Tesla and Beyond
As these strategies unfold, the long-term implications for Tesla’s position in Japan are profound. The revisited subsidy system opens pathways for Tesla’s models, such as the Model 3 and Model Y, to challenge prominent European brands in terms of market leadership by 2027. This transformation underlines the growing importance of policy adaptations and strategic marketing in carving out a prominent place within the global automotive landscape.
In conclusion, while Tesla stands to gain significantly from these developments, the broader ramifications for the Japanese automotive market hint at a wave of transformation that could redefine competitive structures and consumer preferences in the years to come.