Tesla’s Innovative 4680 Battery: A New Era in EV Efficiency
The electric vehicle (EV) landscape is on the cusp of transformation thanks to Tesla’s latest breakthrough in battery technology. The unveiling of the “tabless” 4680 architecture marks a significant leap forward for electric vehicles, addressing long-standing issues with battery thermal management and structural integrity. As the automotive industry adapts to this change, the implications for vehicle design, production, and sustainability are immense and far-reaching.
Disrupting Conventional Battery Design
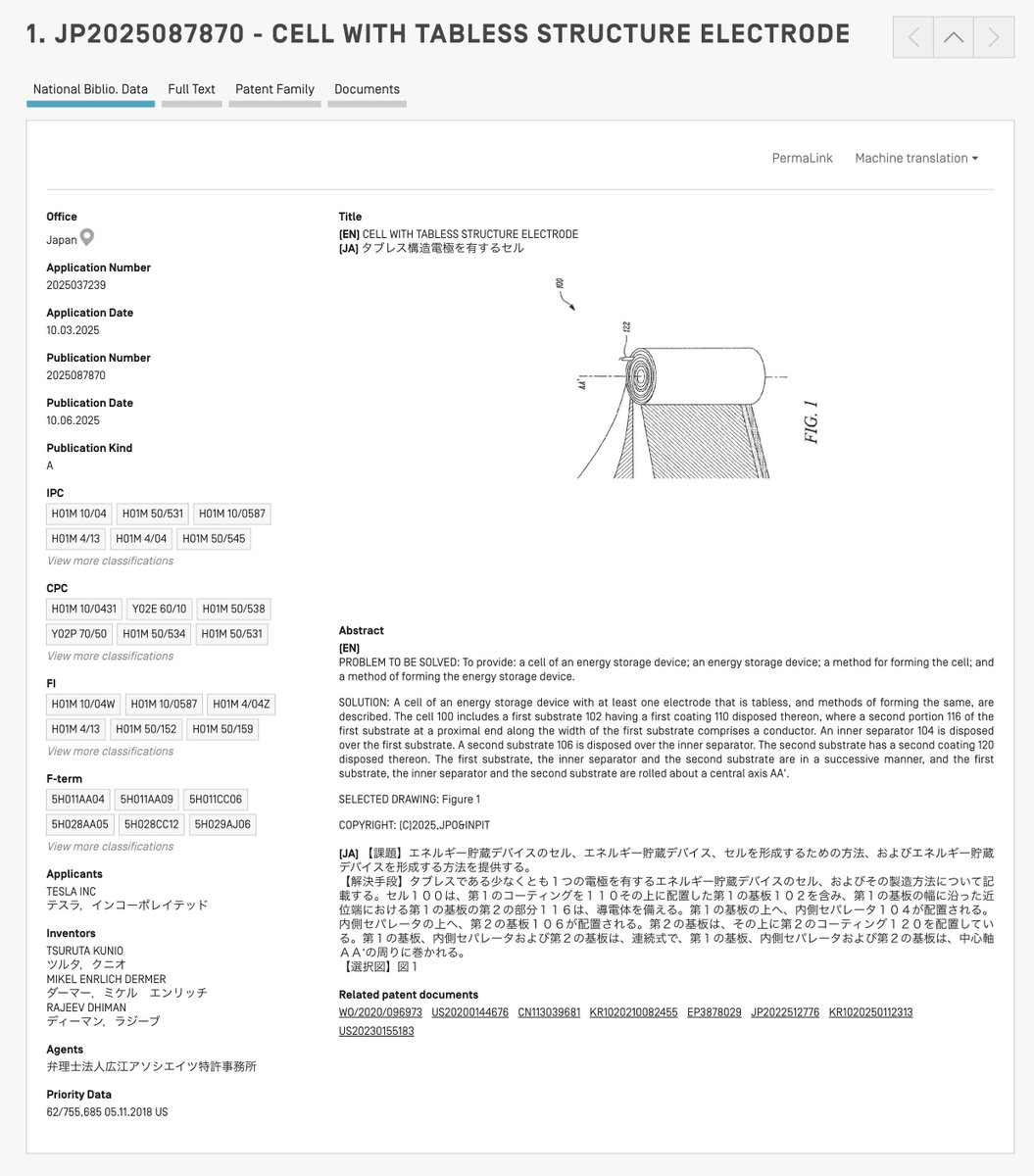
The 4680 cell’s innovation lies in its re-engineering of traditional battery architecture. Historically, lithium-ion batteries have been limited by a design known as the “jellyroll,” a spiral configuration that inherently created thermal bottlenecks. Tesla’s new paradigm shifts away from this restrictive framework, eliminating the singular tab and adopting a continuous metal substrate as a conduit for electric flow.
This architectural advancement ensures a more uniform distribution of current, eradicating hotspots that would otherwise degrade performance over time. The metal substrate mode of operation acts as a comprehensive contact area, enabling electrons to move vertically rather than horizontally, which drastically reduces resistance and heat generation—a critical factor that plagued former designs.
Strategic Timing and Geopolitical Implications
The timing of this technological revelation via a patent filed in Japan aligns with Tesla’s broader strategic goals. As Panasonic scales up battery production efforts in strategic locations such as Wakayama and Kansas, securing intellectual property rights through the Japanese patent system helps Tesla fortify its competitive edge. By ensuring strict adherence to the unique shingled electrode design, Tesla effectively shields itself from competitors who might attempt to replicate their innovations with marginal alterations.
This move not only bolsters Tesla’s position in the fiercely competitive EV market but also cements partnerships that remain compliant with their technological standards, potentially influencing global distribution and production logistics.
Precision Engineering and Design
The success of this “tabless” design is not purely theoretical. Tesla’s engineers have meticulously addressed mechanical challenges to deliver a robust product capable of withstanding real-world conditions. By employing a segmented design with “fingers” that perfectly align to create a shingled contact point, Tesla overcomes the mechanical issues typical of winding larger diameter cells, ensuring electrical reliability and production efficiency.
This design is complemented by a robust structural cap that features intricate spiraled grooves, allowing precise and durable connections capable of withstanding the rigors of automotive environments. Through these engineering feats, Tesla establishes a significant reduction in component failures, enhancing the longevity and reliability of their electric powertrains.
Impact on Vehicle Design and Performance
Beyond the micro-engineering triumph, the macro implications for Tesla’s vehicle design are profound. The innovation enables the creation of “Structural Battery Packs,” which do not merely power the vehicle but become an integral element of its chassis. These structurally integral cells contribute directly to vehicle performance by reducing mass and enhancing structural rigidity, potentially revolutionizing how we think about vehicle assembly and performance.
This new battery architecture also supports the transition to even more powerful charging capabilities, paving the way for future high-performance platforms. Vehicles like the Cybertruck and Tesla Semi stand to benefit immensely, operating at unprecedented efficiency levels while maintaining the rugged capabilities required for heavier payloads.
Forecasting a Sustainable Future
Perhaps one of the most exciting prospects of Tesla’s innovation is its potential impact on sustainability. By minimizing the energy loss associated with resistance and heat production, these new cells promote greater energy efficiency. This breakthrough could see a reduction in the environmental impact of battery production and disposal, aligning with global pushes for sustainable development.
As Tesla’s “tabless” 4680 architecture matures within the mainstream, it sets a benchmark not only for performance but for sustainable practices that could redefine industry norms. More importantly, it presents the automotive industry with a tangible pathway to achieving lower carbon footprints while fulfilling the ever-growing demand for efficient electric mobility solutions.
In conclusion, Tesla’s newly patented advanced battery design redefines the standard for electric vehicle efficiency, creating new possibilities for the future of automotive engineering. As the world embraces electric mobility, such innovations are crucial in shaping a sustainable, technologically advanced future where the possibilities are as limitless as the roads that traverse them.